
MACHINE CONTROLS & MACHINE GUARDING
This is a sample or partial document
Download the full customizable and printable version
Do you know that machine guards on your machine are important to you and your safety as an employee?
Here are some important factors as to why it is important to you as an employee to use safe guards on machines. First, your hands, arms and other parts of your body are vital to you and we all want to protect our physical body from any harm, right?
This is the reason that your company has taken the time to educate you with this orientation on why safe guards should be put on machines. When operating a moving part machine with a safety guard it will prevent the operators hands, fingers and body from any type of danger which could result in serious injury. Any individual who operates this equipment must be trained first and also authorized. Your license means you have received proper training and are capable of safely operating the guard machine. Once you are trained and authorized, the rest is up to you.
You are expected to have the maturity and responsibility to operate the machine efficiently and safely. Don't take this responsibility lightly. A good operator knows why machine guarding is extremely important while operating the machine and that is you first step to safety.
It is crucial to understand why safe guards are to be used on machines. In addition to operators, maintenance workers must be trained and taught how to use the safe guards.
An operator or maintenance worker must be informed as to the location of the safe guards on the machines, and should also be provided information on why safe guards protect them and what hazards they protect them from.
An operator or maintenance worker also should be trained on how to remove safe guards from the machines and also to understand in what circumstances guards can be removed.
Workers need to be trained in procedures to follow if they notice guards are damaged, missing or inadequate.
An operator or maintenance worker should be provided with a dress code. For example; no loose fitting clothing or jewelry. These items could easily be caught in the machines, and remember, safety is everyone's responsibility.
Maintenance workers need to be provided information on up-to-date machines that have been serviced, and they should maintain a record log of this information.
Maintenance workers must also know when to LOCK OUT the machines. This is extremely critical when repairs are being done on the machine. Maintenance workers should also be using safe equipment when doing repair work and they should insure the equipment itself is properly guarded. You are much more productive working safely and obeying safety rules. All we ask is for you to perform your job professionally and safely.
Let's review a few engineering principles so you will have the knowledge to make your own decisions and exercise good judgment.
The first condition for maintenance workers is to be aware of guarding during maintenance. This is perhaps the most hazardous time, and if not aware of certain procedures it can result in large numbers of accidents and injuries. The machine must be put in a state where; if making an unexpected movement which could cause an injury, it would be reduced to a practical minimum.
The purpose of this procedure is to discuss the power lock out. The second condition is the zero-mechanical state or ZMS, where every power source of the machine that can produce movement has been locked off.
The third important principal is RESPONSIBILITY.
The manufacturer should provide information and furnish operation and maintenance instruction with equipment covered by standards and instructions.
Specific operating and maintenance instructions need to be outlined in the maintenance and operating manuals to aid personnel in the safe operation and maintenance of equipment.
The fourth important factor is the EMPLOYER.
They shall be responsible for monitoring employees activities while engaged in trouble shooting and maintenance or repair of machines in an isolated or hidden area.
The employer should also be aware of the equipment which could have mechanical defaults and possible injuries to the safety of the operators. The operator must be placed in an intensive training program of ZMS instructions. This is to teach the operator that it can be very dangerous to enter a machine unless every requirement of ZMS is satisfied.
Persons must not place any part of their body in the path of possible moving machine members during set up, lubrication, adjustments, installation or maintenance. Operators must be trained to respect the possible danger of machine motions.
Operators have to be trained to be aware of possible defects or malfunctions on their machine guards.
It is the responsibility of the employer to recommend a start up procedure that will minimize hazards. The employer will also set up a shut down procedure before allowing any inspection, adjustment or maintenance covered by the standard requirements of ZMS.
Each manager should develop a written program policy for his/her employees to follow, such as rules, specific procedures to follow.
Each initiator and valve. "Manual Override" must be tested to insure that all power sources have been disconnected and that all remaining pressure from the machines have been reduced to prevent unexpected motion of machine members. He must give particular attention to the closed center valves. There should also be plated "Caution" and "Warning" signs posted for operators to be aware of. Employers should also post written policies for ZMS to follow.
Employers should post procedures for placing machine "A" in zero mechanical state where all employees can read and follow daily. The OSHA Act has a major goal to all manufactures to have a machine guard on all machines and equipment used to prevent hazardous injuries to employees.
If the machine you are using has been equipped with a machine guard against hazardous injuries..... in the long run it will save the company a great deal of money. Guarding terminology - and the lack of meanings of terms can cause accidents and injuries.
Built in guards are machines purchased with a safety guard already attached to the machine. OSHA Compliance Check Lists for guarding can be a system that prevents injuries. The check list will list individually all machines and equipment used. For each unit machine it will list the point of operation and power transmission components. It should state if the machines are safety guarded or not.
If machine is guarded, does it meet OSHA requirements - and what type of guarding is used, such as enclosure, fencing, or location. Most production machines will require some form of enclosure of the hazard points to comply with OSHA requirements.
Guards and noise controls, are another important principal to be used on machines to help absorb or reflect sound waves. For noise reduction, manufactures have built home made guards that can be designed as a barrier for noise as well as a barrier against personal injury.
Machines can produce only it they are used correctly, and they are used correctly only when all guards and safe guards are in place.
So in brief, a complete guarding program is essential for any company. It prevents accidents, either to operators or machines, and thus facilitates production goals. So, with this understanding and knowledge it will help prevent hazardous injuries on the job.
The techniques of guarding a hazard creating motion may be guarded by several ways, such as guarding, reciprocating, or transverse motions.
The techniques of guarding various action when using tools to perform work, such as cutting, bending, punching, would be the guarded motion approach which is used to drive or power the tool when using it.
Here are some requirements that you need to be aware of when operating a machine.
First, all machines, parts of machines, or component parts that you are using which create hazards are required to be safety guarded.
There also has to be an opening through guards or enclosures within two inches of the moving part to preclude passage of any objects one-half inch in diameter.
All operators should have free access to the power control buttons in case of an immediate emergency. Machine power controls shall be kept up in a safe operating condition. The machine power controls shall be located and installed at a proper location whey they can't operate from accidental contact, with objects or parts of the body. They should also be located for the operator, so it's near his working position.
All power control buttons and switches will be color coded as follows;
Start, Run or Inch - Black, Green or Silver.
Emergency stop - RED
Cycle Stop or Auto Stop - Yellow or Red.
All power control buttons and switches will be properly identified to its function and purpose.
When working on electrical equipment hazards can occur, such as, starting of motors. This is why it is important for the operator to be aware of whether the circuit is opened at the switch box, and the switch should be padlocked in the OFF position and tagged with a work to be done tag on the equipment, the name of the person working on it, and the department involved.
All this information must be written on the tag, this will enhance positive protection.
So remember ....., train your staff right, safely and efficiently. Monitor all employees safety requirements and day to day check up on your performance. Remember anyone can write up a warning tag saying "in repair" but this is not the way for a positive, reassuring protection from locking out equipment.
The supervisor should give detailed procedures to be followed and he should insure that maintenance crews are supplied with and use the right protective equipment.
Maintenance personnel must constantly be on guard when they are working around electrical equipment and circuits, in order to prevent accidental grounding.
Employees also need to have the knowledge of the warning signs, guards and other protective devices. Supervisors should give training on some existing or electric hazard machine, and how to go about it.

GET INSTANT ACCESS
to THE MEMBERS LIBRARY
Safety materials created by safety professionals.
Access to the Safety Manager software.
Wide variety of safety videos and courses.
**Brand New** Safety Training Management System
Pre-Made Safety Materials Ready For Use
Created by experienced safety professionals & risk consultants. Saving you time, money, and risk of injuries.
95% of the work already done.
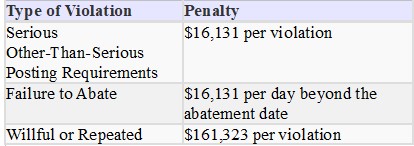
Below are the maximum penalty amounts, with the annual adjustment for inflation, that may be assessed after Jan. 15, 2024. (See OSHA Memo, Jan. 8, 2024).
**New OSHA HEAT 90 DAY**
>>Download Free HERE<<
**New 2024 OSHA 300 Form**
>>Download Free HERE<<
**Brand New**
Free with full membership subscription
Training LMS System
Ask The Safety Consultant
Safety Equipment Deal Finder

“SafetyInfo.com is the first go-to website for safety professionals and companies to use in establishing a solid safety program"
-Mike McKenzie, Certified Safety & Health Manager (CSHM), McSafety Solutions™
Note: You must have a full subscription to the Safety Library in order to use this material. Any use outside of your organization, for resell, or without an active membership is strictly prohibited and may result in prosecution under copyright infringement laws. Please contact us first, if you would be interested in reselling or using our materials for reproduction.
Inside the Members Library
Topic Index
Accident Prevention
Air Quality
Asbestos
Bloodborne Pathogens
Boilers
Chemical Safety
Compressed Gas
Confined Space
Construction
Construction Worksite
Cranes & Slings
Driver / Fleet Safety
Drug Free Workplace
Electrical
Emergency Management
Engineering Safety
Environmental
Equipment
Ergonomics
Fall Protection
Fire Safety & Prevention
First Aid
Flammable Materials
Forklifts
Hazard Communication
Hazardous Materials
Hearing Protection
Heat Stress
Hot Work
Housekeeping
Job Safety Analysis
Laboratory
Ladders
Lead
Lockout-Tagout
Machinery & Equipment
Material Handling
MSDS (SDS)
Medical & First Aid
Occupational Health
Office Safety
Off the Job Safety
Personal Protection
Process Safety
Record Keeping
Respiratory Protection
Silica Safety
Rules & Policies
Signs & Labels
Slips, Trips & Fall
Training
Terrorism Programs
Tool Safety
Vehicle & Driver
Violence Programs
Welding & Hot Work
Training Videos
Library Index
Training Materials
Videos/Courses
Talks
Articles
PowerPoint
Handouts
Training Overheads
Quizzes
Supervisor Briefs
Management Briefs
Safety Sessions
2 Minute OSHA Safety Talks
Pamphlets
First Aid Training
Supervisor Training
Hazardous Materials
Bomb Threat
Crossword Puzzles
Biological Agents
Forms & Documents
Forms
Checklists
Audit Guides
Inspections Guides
Signs & Labels
Environmental Audit Guides
Recordkeeping - OSHA 300
Sign & Label Maker
Safety Management Resources
Safety Manuals/Written Programs
Ergonomic Programs
Emergency Plans
Process Safety Management
Construction Safety
Occupational Health
Environmental
Topic Sheets
DOT Fleet-Driver
Hazardous Materials
Chemical Safety
Drug Free Workplace
Terrorism Programs
Development Guides
Safety Manager Software
Safety References & Graphics
Technical Safety Information
Posters
Topic & Fact Sheets
Development Information
Job Specific Safety Rules
Terrorism
Calculators
Safety Comic Strips
New Safety Training System
Schedule and train your employees with our materials. Add unlimited amount of employees. Record all progress and issue certificates. For group and individual training sessions.

