
Hot Work Workplace Safety Program
Purpose
Welding and Hot Work, such as brazing or grinding present a significant opportunity for fire and injury. All precautions of this program must be applied prior to commencing any welding or hot work by company employees or contractors. Reference: OSHA 29 CFR 1910.252
Responsibilities
Management
• Provide training for all employees whose task include heat, spark or flame producing operations such as welding, brazing, or grinding.
• Develop and monitor effective hot work procedures
• Provide safe equipment for hot work
• Provide proper and effective PPE for all hot work
Supervisors
• Monitor all hot work operations
• Ensure all hot work equipment and PPE are in safe working order
• Allow only trained and authorized employees to conduct hot work
• Ensure permits are used for all hot work outside authorized areas
Employees
• Follow all hot work procedures
• Properly use appropriate hot work PPE
• Inspect all hot work equipment before use• Report any equipment problems
• Not use damaged hot work equipment
Definitions
Welding/Hot Works Procedures: any activity which results in sparks, fire, molten slag, or hot material which has the potential to cause fires or explosions.
Examples of Hot Works: Cutting, Brazing, Soldering, Thawing Pipes, Torch Applied Roofing, Grinding and Welding.
Special Hazard Occupancies: Any area containing Flammable Liquids, Dust Accumulation, Gases, Plastics, Rubber and Paper Products.
Hazards
• Fires & Explosions
• Skin burns
• Welding "blindness"
• Respiratory hazards from fumes & smoke
Training
Training shall include:
• Review of requirements listed in OSHA 1910.252
• Use of Hot Works Permit System
• Supervisor Responsibilities
• Fire Watch Responsibilities - specifically, the fire watch must know:
1. That their ONLY duty is Fire Watch
2. When they can terminate the watch
3. How to use the provided fire extinguisher
4. How to activate fire alarm if fire is beyond the incipient stage
• Operator Responsibilities
• Contractors Responsibilities
• Documentation requirements
• Respirator Usage requirements
• Fire Extinguisher training
Hot Works Procedures
OSHA 29 CFR 1910.252 required fire prevention actions for welding/hot works.
Where practicable all combustibles shall be relocated at least 35 feet from the work site. Where relocation is impractical, combustibles shall be protected with flame proof covers, shielded with metal, guards, curtains, or wet down material to help prevent ignition of material.
Ducts, conveyor systems, and augers that might carry sparks to distant combustibles shall be protected or shut down.
Where cutting or welding is done near walls, partitions, ceilings, or a roof of combustible construction, fire-resistant shields or guards shall be provided to prevent ignition.
If welding is to be done on a metal wall, partition, ceiling, or roof, precautions shall be taken to prevent ignition of combustibles on the other side, due to conduction or radiation of heat. Where combustibles cannot be relocated on the opposite side of the work, a fire watch person shall be provided on the opposite side of the work.
Welding shall not be attempted on a metal partition, wall, ceiling or roof having a covering nor on walls having combustible sandwich panel construction.
Cutting or welding on pipes or other metal in contact with combustible walls, partitions, ceilings, or roofs shall not be undertaken if the work is

GET INSTANT ACCESS
to THE MEMBERS LIBRARY
Safety materials created by safety professionals.
Access to the Safety Manager software.
Wide variety of safety videos and courses.
**Brand New** Safety Training Management System
Pre-Made Safety Materials Ready For Use
Created by experienced safety professionals & risk consultants. Saving you time, money, and risk of injuries.
95% of the work already done.
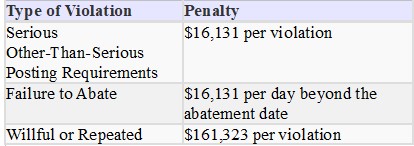
Below are the maximum penalty amounts, with the annual adjustment for inflation, that may be assessed after Jan. 15, 2024. (See OSHA Memo, Jan. 8, 2024).
**New OSHA HEAT 90 DAY**
>>Download Free HERE<<
**New 2024 OSHA 300 Form**
>>Download Free HERE<<
**Brand New**
Free with full membership subscription
Training LMS System
Ask The Safety Consultant
Safety Equipment Deal Finder

“SafetyInfo.com is the first go-to website for safety professionals and companies to use in establishing a solid safety program"
-Mike McKenzie, Certified Safety & Health Manager (CSHM), McSafety Solutions™
Note: You must have a full subscription to the Safety Library in order to use this material. Any use outside of your organization, for resell, or without an active membership is strictly prohibited and may result in prosecution under copyright infringement laws. Please contact us first, if you would be interested in reselling or using our materials for reproduction.
Inside the Members Library
Topic Index
Accident Prevention
Air Quality
Asbestos
Bloodborne Pathogens
Boilers
Chemical Safety
Compressed Gas
Confined Space
Construction
Construction Worksite
Cranes & Slings
Driver / Fleet Safety
Drug Free Workplace
Electrical
Emergency Management
Engineering Safety
Environmental
Equipment
Ergonomics
Fall Protection
Fire Safety & Prevention
First Aid
Flammable Materials
Forklifts
Hazard Communication
Hazardous Materials
Hearing Protection
Heat Stress
Hot Work
Housekeeping
Job Safety Analysis
Laboratory
Ladders
Lead
Lockout-Tagout
Machinery & Equipment
Material Handling
MSDS (SDS)
Medical & First Aid
Occupational Health
Office Safety
Off the Job Safety
Personal Protection
Process Safety
Record Keeping
Respiratory Protection
Silica Safety
Rules & Policies
Signs & Labels
Slips, Trips & Fall
Training
Terrorism Programs
Tool Safety
Vehicle & Driver
Violence Programs
Welding & Hot Work
Training Videos
Library Index
Training Materials
Videos/Courses
Talks
Articles
PowerPoint
Handouts
Training Overheads
Quizzes
Supervisor Briefs
Management Briefs
Safety Sessions
2 Minute OSHA Safety Talks
Pamphlets
First Aid Training
Supervisor Training
Hazardous Materials
Bomb Threat
Crossword Puzzles
Biological Agents
Forms & Documents
Forms
Checklists
Audit Guides
Inspections Guides
Signs & Labels
Environmental Audit Guides
Recordkeeping - OSHA 300
Sign & Label Maker
Safety Management Resources
Safety Manuals/Written Programs
Ergonomic Programs
Emergency Plans
Process Safety Management
Construction Safety
Occupational Health
Environmental
Topic Sheets
DOT Fleet-Driver
Hazardous Materials
Chemical Safety
Drug Free Workplace
Terrorism Programs
Development Guides
Safety Manager Software
Safety References & Graphics
Technical Safety Information
Posters
Topic & Fact Sheets
Development Information
Job Specific Safety Rules
Terrorism
Calculators
Safety Comic Strips
New Safety Training System
Schedule and train your employees with our materials. Add unlimited amount of employees. Record all progress and issue certificates. For group and individual training sessions.

