
Hydro-blast - High-Pressure Water Cleaning Workplace Safety Program
Purpose
This program outlines the minimum requirements that will be met by Company Name and contractors/subcontractors when performing high-pressure water cleaning (HPWC).
Responsibilities
Management
◦ Provide proper equipment and procedures
◦ Provide safety training for all operators of HP Water systems
◦ Perform periodic inspections and audits
Supervisors
◦ Oversee all operations involving use of high pressure water
◦ Ensure equipment is safe prior to use
◦ Allow only qualified employees to operate equipment
◦ Ensure areas are safe for passers by
Contractors
◦ Ensure all equipment meets the requirements of this program
◦ Provide contractor employees with certification training
◦ Maintain records of maintenance and training
◦ Provide safety controls at all work sites
DEFINITIONS
High-pressure water cleaning: The use of high-pressure water, with or without the addition of other liquids or solid particles, to remove unwanted matter from various surfaces.
High-pressure water cleaning systems: Water delivery systems, which have nozzles or other openings whose function is to increase the speed of liquids. Solid particles or additional chemicals may also be introduced, but the exit in all cases will be a free stream. The system includes pumps (pressure reducing devices) and the hoses, lances, nozzles, valves and safety devices as well as any heating elements or injection systems attached thereto.
High-pressure water cutting: The use of high-pressure water, with or without the addition of other liquids or solid particles, to penetrate into surfaces of a material for the purpose of cutting that material.
Line moling: An operation using a self-propelled jet nozzle (mole) and a high-pressure hose to clean the inside of piping systems.
Dump valve: A device that immediately shuts down the high-pressure water stream if the operator loses control. Used in tube lancing and line moling water cleaning methods.
Lance: A rigid metal tube used to extend the nozzle from the end of a hose.
SAFETY
High-pressure water cleaning is normally performed using jet streams that can have a velocity greater than that of a 45-caliber bullet, and do as much damage. Therefore, extreme caution and strict compliance with procedures must be used to prevent the jet stream from striking the operator, other employees or delicate equipment. No portion of the body must ever be placed in front of the water jet. These jets of water can easily puncture and tear the skin or penetrate deeper causing infection or serious internal damage. Horseplay with such equipment is strictly forbidden. Violators will be disciplined and subject to immediate termination.
PERSONAL PROTECTIVE EQUIPMENT
Personnel performing high-pressure water cleaning that are exposed to water spray or reflected material will wear a raincoat, rubber pants, safety glasses, hardhat with face shield, rubber boots and gloves. Hearing protection will also be worn. These do NOT provide protection from the jet but do protect against hazards encountered while performing the work.
The following identifies at a minimum the personal protective equipment that will be issued to employees performing high-pressure water cleaning outside of the required hardhat and safety glasses with side shields:
Face shields – Clear shield nine inches deep by fifteen and one-half inches wide by 0.60 thick (ANSI Z87.1-1979 or equivalent).
Rain Suit – Made of nylon fabric coated with Neoprene on both sides.
Gloves – Made of Neoprene, rubber and PVC with rough wet grip finish.
Rubber steel-toed boots – Knee length with ribbed steel shanks and heavy tread soles for nonslip traction (ANSI Z41.1-1967 or equivalent).
Metatarsal Guards – Designed to be worn with lace-type steel toe boots.
When cleaning equipment which could possible be contaminated with hazardous chemicals, appropriate additional protection specified by the project management/safety will be worn by the operator as well as other employees who may be affected.
When tube lancing or "shotgunning", boots provided with steel toecaps and metatarsal protection will be worn.
NOTE: At operating pressures over 5,000 psi and above, employees are required to wear protective suits made of Kevlar.
PROCEDURE
The High-Pressure Water Cleaning Job Qualification form (see forms section) must be completed prior to performing any high-pressure water cleaning to determine if there are alternate methods for performing the task that are less hazardous.
The HPWC system will be depressurized when:
• Not in use.
• Unauthorized or inadequately protected personnel enter the barricaded area.
• Replacement or repairs are made to the system.
• Recommended practices are violated.
Any incident, near miss or abnormal occurrence will be immediately reported to the responsible supervisor and an investigation conducted.
A cleaning crew will be composed of at least two operators. Each crew member will be in view of another crew member at all times.
Operators will not operate equipment for more than eight (8) consecutive hours in any sixteen (16) hour period. The team members should rotate their duties during the job to minimize fatigue to the operator holding the tools.
The equipment operator nearest the high-pressure nozzle must always have a means of immediately reducing pressure or interrupting the flow to the nozzle.
When the hose drop exceeds ten (10) feet, the hose will be securely tied off to a rigid support with a fiber rope to limit the pull due to hose weight. Bend radius limits (as identified by the manufacturer) must be maintained.
At least one control valve or switch will control each high-pressure tool. An employee will operate only one high-pressure lance, mole or shotgun at one time.
At least one control valve or switch will control each high-pressure tool. An employee will operate only one high-pressure lance, mole or shotgun at one time.
The area around the job, pump and hoses will be barricaded a minimum of fifteen (15) feet and signs stating "DANGER – HIGH-PRESSURE WATER CLEANING" must be placed at the perimeters. Barricades may be of rope, tape, barrels, etc. as long as they give an effective warning and are highly visible.
If the job is above ground level, barricades may be required below. Warning signs should be placed along those portions of the high-pressure water hose, which are outside the barricades. When line moling, all pipe openings will be properly barricaded.
High-pressure cleaning hose will be positioned and handled to minimize bends and turns. Sharp bends and turns can result in hose failure.
High-pressure hose connections will have safety cables, chains or the equivalent bridging at each joint.
High-pressure water cleaning equipment must be designed and maintained to achieve a minimum safety factor of three to one (3:1) against maximum allowable working pressure.
Hose data, i.e. manufacturer’s symbol, serial number, working and test pressure and certified rating, which will provide a safety factor of 3 to 1 against burst will be recorded and retained in the project’s central files.
The supervisor responsible for the job will fill out the High-Pressure Water Cleaning Equipment Checklist form before starting each job.
The pressure must be removed from the system before tightening or loosening fittings.
When the hose is pressurized, personnel must not handle the hose within one foot of the hose-to-hose connections.
Back thrust:
Reactive back thrust forces from the high-pressure water jets physically stress the operator and affects operator control. Sound footing conditions must be established and maintained during cleaning.
Back thrust forces results from water leaving the nozzle at a high velocity. During manual shotgun cleaning operations, back thrust can be calculated from the equation below.
Back Thrust (lb) – 0.052 Q t P
Where: Q-Flow Rate in U.S. gallons/minute
P – Jet Pressure Measured in PSI
For determining GPM, use the equation:
Q-{29.9(K) D2) (tP)}
Where K – 0.09 constant
Operators of the shotgun-type equipment will not be required to withstand a back thrust or more than one-third (1/3) of their body weight.
If the area to be blasted is in a confined space or the operator must climb to an elevated position such as on a ladder or scaffolding, it is required that a safety harness be used. Railings or other protection should be provided.
Do
DO wear protective clothing.
DO stop unit to change nozzle, hose assemblies and other parts.
DO stop unit in case of a leak.
DO wear a safety harness when in an elevated position.
DO use only the manufacturer’s recommended chemicals.
DO use sediment – free water.
Don't
DON’T tie gun lever or trigger down.
DON’T start the unit with the gun engaged.
DON’T aim the gun at people, light unsecured objects or other potential hazards.
DON’T engage gun unless it is properly connected and held.
DON’T lay the gun in mud, dirt or sand.
Equipment: Setup, Inspections & Testing
An automatic relief device will be installed on the high-pressure side of the pump set to relieve at not higher than the maximum allowable working pressure of the lowest rated component in the high-pressure system and will be tested annually. Documentation will be maintained on the test results.
Prior to starting the job, a visual inspection of the high-pressure components (including rupture disk pressure rating) should be performed and documented. Hose with exposed or damaged wire braid will be removed from high-pressure service. The assembled high-pressure water cleaning components will be SLOWLY pressurized to the maximum operating pressure to verify integrity of the system.
A hose inspection and testing program (per manufacturer’s guidelines) will be conducted at least quarterly. The inspection test will be conducted at 1 ½ times the maximum operating pressure and will be observed and documented by personnel responsible for the site procedure.
Hose failures usually occur near fittings due to bending stresses during use and handling. Pressurized hoses will NOT be handled within one foot of hose-to-hose connections. Hose-to-tool connections, which are in frequent contact with the operator, must be shielded by a shroud to protect the operator. These shrouds must have sufficient rigidity to resist bending to radius smaller than those recommended by the hose manufacturers.
Maintenance
Competent (designated in writing) employees will conduct servicing in accordance with manufacturer’s servicing requirements.
The following items will be overhauled and inspected for proper functioning at the manufacturer’s recommended intervals:
• Pressure relief valve
• Bursting discs (if used)
• Pressure control valves
• Hand or foot operated dump control valve or dry shut-off valve
• Dry shut-off valve or dump systems
• Changeover valve
Tools
When maintaining or assembling high-pressure water cleaning systems, the correct size tool MUST be used. The use of adjustable tools having serrated gripping jaws (i.e. pipe wrenches), which can damage equipment, will NOT be used.
NOTE: Only manufacturer’s parts may be used for repairs to equipment. Manufacturer’s equipment will not be altered or modified under any circumstances.
High Pressure Water Cleaning Methods
Lancing, line moling and shotgunning are the basic high-pressure water cleaning methods. Different variations of each method are available and increasing with new technology. Rotating nozzle assemblies, rotating lances and orbital nozzles are some variations available at this time.
Rotating equipment such as lances and nozzle tips must be guarded to prevent contact and injury to operating personnel. Loose clothing, which can be caught in rotating equipment, is NOT permitted.
Tube Lancing
Tube lancing is a repetitive operation using a rigid or flexible lance to clean the inside of tube bundles.
High-pressure water flow to the lance will be actuated through a fail-safe, contact-type switch or foot-operated dump valve which, when released by the lance operator, interrupts pressure at the lance. The valve or switch must have a guard to prevent inadvertent actuation. Use of foot-operated dump valve is required.
A hand-held deflector or guard will be installed on the lance to prevent the high-pressure stream from contacting the operator’s hand is the lance is accidentally withdrawn from a tube while activated. The inside diameter of the deflector or guard will be less than the outside diameter of the jet nozzle so that the nozzle cannot inadvertently slip through the guard and contact the operator.
An easily visible marker will be affixed two feet from the nozzle end of the lance to indicate nozzle location, as the lance is being inserted or withdrawn from the tube.
NOTE: Pressure will be applied to the nozzle only when the lance is two feet inside the tube.
The back end of the tube or shell will be shrouded to guard personnel from the jet stream, discharged contaminants and ejected nozzles.
Line Moling
Line moling is an operation using a self-propelled nozzle (mole) and a high-pressure hose to clean the inside of piping systems.
High-pressure water to the mole will be controlled by a fail-safe, contact-type switch or foot-operated dump valve switch, when released by the operator nearest the mole, interrupts flow to the mole. The valve or switch will have a guard to prevent inadvertent actuation. Use of a foot-operated dump valve is required.
To prevent mole reversal within the line, the length of the hose end coupling, mole tip and any rigid pipe extensions will equal or exceed the inside diameter of the pipe being cleaned.
The mole hose will be marked two feet from the mole to indicate mole location when the hole location is inserted or

GET INSTANT ACCESS
to THE MEMBERS LIBRARY
Safety materials created by safety professionals.
Access to the Safety Manager software.
Wide variety of safety videos and courses.
**Brand New** Safety Training Management System
Pre-Made Safety Materials Ready For Use
Created by experienced safety professionals & risk consultants. Saving you time, money, and risk of injuries.
95% of the work already done.
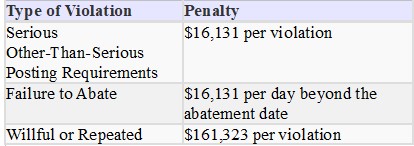
Below are the maximum penalty amounts, with the annual adjustment for inflation, that may be assessed after Jan. 15, 2024. (See OSHA Memo, Jan. 8, 2024).
**New OSHA HEAT 90 DAY**
>>Download Free HERE<<
**New 2024 OSHA 300 Form**
>>Download Free HERE<<
**Brand New**
Free with full membership subscription
Training LMS System
Ask The Safety Consultant
Safety Equipment Deal Finder

“SafetyInfo.com is the first go-to website for safety professionals and companies to use in establishing a solid safety program"
-Mike McKenzie, Certified Safety & Health Manager (CSHM), McSafety Solutions™
Note: You must have a full subscription to the Safety Library in order to use this material. Any use outside of your organization, for resell, or without an active membership is strictly prohibited and may result in prosecution under copyright infringement laws. Please contact us first, if you would be interested in reselling or using our materials for reproduction.
Inside the Members Library
Topic Index
Accident Prevention
Air Quality
Asbestos
Bloodborne Pathogens
Boilers
Chemical Safety
Compressed Gas
Confined Space
Construction
Construction Worksite
Cranes & Slings
Driver / Fleet Safety
Drug Free Workplace
Electrical
Emergency Management
Engineering Safety
Environmental
Equipment
Ergonomics
Fall Protection
Fire Safety & Prevention
First Aid
Flammable Materials
Forklifts
Hazard Communication
Hazardous Materials
Hearing Protection
Heat Stress
Hot Work
Housekeeping
Job Safety Analysis
Laboratory
Ladders
Lead
Lockout-Tagout
Machinery & Equipment
Material Handling
MSDS (SDS)
Medical & First Aid
Occupational Health
Office Safety
Off the Job Safety
Personal Protection
Process Safety
Record Keeping
Respiratory Protection
Silica Safety
Rules & Policies
Signs & Labels
Slips, Trips & Fall
Training
Terrorism Programs
Tool Safety
Vehicle & Driver
Violence Programs
Welding & Hot Work
Training Videos
Library Index
Training Materials
Videos/Courses
Talks
Articles
PowerPoint
Handouts
Training Overheads
Quizzes
Supervisor Briefs
Management Briefs
Safety Sessions
2 Minute OSHA Safety Talks
Pamphlets
First Aid Training
Supervisor Training
Hazardous Materials
Bomb Threat
Crossword Puzzles
Biological Agents
Forms & Documents
Forms
Checklists
Audit Guides
Inspections Guides
Signs & Labels
Environmental Audit Guides
Recordkeeping - OSHA 300
Sign & Label Maker
Safety Management Resources
Safety Manuals/Written Programs
Ergonomic Programs
Emergency Plans
Process Safety Management
Construction Safety
Occupational Health
Environmental
Topic Sheets
DOT Fleet-Driver
Hazardous Materials
Chemical Safety
Drug Free Workplace
Terrorism Programs
Development Guides
Safety Manager Software
Safety References & Graphics
Technical Safety Information
Posters
Topic & Fact Sheets
Development Information
Job Specific Safety Rules
Terrorism
Calculators
Safety Comic Strips
New Safety Training System
Schedule and train your employees with our materials. Add unlimited amount of employees. Record all progress and issue certificates. For group and individual training sessions.

