
Lead Workplace Safety Program
Purpose
The purpose of the Company's Lead Safety Program is to protect both our employees and the environment from lead contamination from our facility operations. The intent of our program is to be in full, continuous compliance with OSHA Standard 29 CFR 1910.1025 and all other local, State and Federal requirements for our industry.
Responsibilities
Management will implement, maintain & monitor effectiveness of:
• entire lead safety program, including semi-annual revisions and updates to reflect the current status of the program
• engineering & administrative controls for lead exposure
• employee training and awareness• medical surveillance program
• respiratory protection program
• lead disposal program
• housekeeping program
• protective clothing issue, storage and disposal
Supervisors will:
• provide effective and continuous control of all lead operations
• immediately inform management of any deficiencies in engineering or administrative controls
• conduct routine assigned inspections and monitoring
• immediate correct any deviation from operational safety requirements
• provide immediate on-the-spot training for any employee who shows lack of knowledge or application of required operational lead safety requirements
• ensure all employees are properly trained before commencing any operation that may contribute to lead exposure
Employees will:
• follow all operational and lead safety procedures
• seek immediate supervisor guidance to resolve questions
• conduct operations in accordance with company provided training
• immediately report to a supervisor any deficiency in engineering or administrative controls
• properly use, store and dispose of issued and assigned personal protective clothing.
• maintain change and shower areas neat and orderly
Process, Control & Technical Information
The following information that describes facility specific information concerning processes and controls are maintained as an addendum to this written program:
a. Description of each operation in which lead is emitted; e.g. machinery used, material processed, controls in place, crew size, employee job responsibilities, operating procedures and maintenance practices.
b. Description of the specific means used to achieve compliance, including engineering plans and studies used to determine methods selected for controlling exposure to lead.
c. Report of the technology considered in meeting the permissible exposure limit;
d. Air monitoring data which documents the source of lead emissions;
e. A detailed schedule for implementation of this program, including documentation such as copies of purchase orders for equipment, construction contracts, etc.
f. Records of Employee Training and Notifications
g. Specific work practice program and controls for each operation involving lead exposure
h. Administrative control schedule
i. All other relevant information
Hazards
Pure lead (Pb) is a heavy metal at room temperature and pressure and is a basic chemical element. It can combine with various other substances to form numerous lead compounds. The Permissible Exposure Limit (PEL) set by OSHA is 50 micrograms of lead per cubic meter of air (50 ug/m(3)), averaged over an 8-hour workday.
Lead can be absorbed by inhalation (breathing) and ingestion (eating). Lead is not absorbed through your skin. When lead is scattered in the air as a dust, fume or mist it can be inhaled and absorbed through the lungs and upper respiratory tract. Lead can also be absorbed through the digestive system if swallowed. Handling food, cigarettes, chewing tobacco, or make-up which have lead contamination or handling them with hands contaminated with lead, will contribute to ingestion.
A significant portion of inhaled or ingested lead goes into the blood stream. Once in the blood stream, lead is circulated throughout the body and stored in various organs and body tissues. Some of this lead is quickly filtered out of the body and excreted, but some remains in the blood and other tissues. As exposure to lead continues, the amount stored in the body will increase. Lead stored in body tissues can cause irreversible damage, first to individual cells, then to organs and whole body systems.
Short-term (acute) effects of overexposure to lead
Lead is a potent, systemic poison. Taken in large enough doses, lead can kill in a matter of days. A condition affecting the brain called acute encephalopathy may arise which develops quickly to seizures, coma, and death from cardiorespiratory arrest. There is no sharp dividing line between rapidly developing acute effects of lead, and chronic effects which take longer to acquire. Lead adversely affects numerous body systems, and causes forms of health impairment and disease which arise after periods of exposure as short as days or as long as several years.
Long-term (chronic) effective of overexposure to lead.
Chronic overexposure to lead may result in severe damage to blood-forming, nervous, urinary and reproductive systems. Some common symptoms of chronic overexposure include loss of appetite, metallic taste in the mouth, anxiety, constipation, nausea, pallor, excessive tiredness, weakness, insomnia, headache, nervous irritability, muscle and joint pain or soreness, fine tremors, numbness, dizziness, hyperactivity and colic. In lead colic there may be severe abdominal pain.
Monitoring
Initial determination. The company has made an initial determination of lead work areas and exposure levels and will conduct subsequent "initial determinations" in the event of changes to hazard control methods or operational processes that affect employee or environmental exposure. Initial determinations are conducted to determine if any employee may be exposed to lead at or above the action level of 30 micrograms per cubic meter of air (30 ug/m(3)) averaged over an 8-hour period.
Where a determination is made that no employee is exposed to airborne concentrations of lead at or above the action level, the company shall maintain a written record. The record shall include quantitative sampling data, date of determination, location within the worksite, and the name and social security number of each employee monitored.
Monitoring requirements
Monitoring and analysis methods shall have an accuracy (to a confidence level of 95%) of not less than plus or minus 20 percent for airborne concentrations of lead equal to or greater than 30 ug/m(3).
Where a determination shows the possibility of any employee exposure at or above the action level, the company shall conduct monitoring which is representative of the exposure for each employee in the workplace or process area who is exposed to lead.
For the purposes of monitoring requirements, employee exposure is that exposure which would occur if the employee were not using a respirator.
Monitoring and sample collection shall cover full shift (for at least 7 continuous hours) personal samples including at least one sample for each shift for each job classification in each work area.
Full shift personal samples must be representative of the monitored employee's regular, daily exposure to lead.
Monitoring Frequency
At or Above Action Level and Below PEL. Every 6 months ff the initial determination or subsequent monitoring reveals employee exposure to be at or above the action level but below the permissible exposure limit. This monitoring (6 month frequency) will continue until at least two consecutive measurements, taken at least 7 days apart, are below the action level.
Above PEL. If the initial monitoring reveals that employee exposure is above the permissible exposure limit the company will repeat monitoring quarterly. Quarterly monitoring will continue until at least two consecutive measurements, taken at least 7 days apart, are below the PEL but at or above the action level.
Additional monitoring. Whenever there has been a production, process, control or personnel change which may result in new or additional exposure to lead, or whenever any other reason to suspect a change which may result in new or additional exposures to lead, additional monitoring will be conducted.
Employee Notification of Monitoring Results.
Within 5 working days after the receipt of monitoring results, each employee will be notified in writing of the results which represent that employee's exposure.
Whenever the results indicate that the representative employee exposure, without regard to respirators, exceeds the permissible exposure limit, the the written notice will include a statement that the permissible exposure limit was exceeded and a description of the corrective action taken or to be taken to reduce exposure to or below the permissible exposure limit.
Observation of monitoring
The company provides affected employees or their designated representatives an opportunity to observe any monitoring of employee exposure to lead.
Observation procedures. Whenever observation of the monitoring of employee exposure to lead requires entry into an area where the use of respirators, protective clothing or equipment is required, the company will provide the observer with and assure the use of respirators, clothing and equipment required, and will require the observer to comply with all other applicable safety and health procedures.
Without interfering with the monitoring, observers is entitled to:
• Receive an explanation of the measurement procedures
• Observe all steps related to the monitoring of lead performed at the place of exposure
• Record the results obtained or receive copies of the results when returned by the laboratory
Engineering Controls
Where any employee is exposed to lead above the permissible exposure limit for more than 30 days per year, the company will implement feasible engineering and work practice controls (including administrative controls) to reduce and maintain employee exposure to lead. Wherever the engineering and work practice controls which can be instituted are not sufficient to reduce employee exposure to or below the permissible exposure limit, the company will still use them to reduce exposures to the lowest feasible level and shall supplement them by the use of respiratory protection.
Where any employee is exposed to lead above the permissible exposure limit, but for 30 days or less per year, the company will implement engineering controls to reduce exposures to 200 ug/m(3), but thereafter may implement any combination of engineering, work practice (including administrative controls), and respiratory controls to reduce and maintain employee exposure to lead to or below 50 ug/m(3).
Mechanical ventilation
When ventilation is used to control exposure, measurements which demonstrate the effectiveness of the system in controlling exposure, such as capture velocity, duct velocity, or static pressure shall be made at least every 3 months. Measurements of the system's effectiveness in controlling exposure shall be made within 5 days of any change in production, process, or control which might result in a change in employee exposure to lead.
Recirculation of air. If air from exhaust ventilation is recirculated into the workplace, the system must include:
• a high efficiency filter with reliable back-up filter; and
• controls to monitor the concentration of lead in the return air and to bypass the recirculation system automatically if it fails are installed, operating, and maintained.
Administrative Controls
If administrative controls are used as a means of reducing employees TWA exposure to lead, the company shall establish and implement a job rotation schedule which includes:
• Name or identification number of each affected employee
• Duration and exposure levels at each job or work station where each affected employee is located
• Other information which may be useful in assessing the reliability of administrative controls to reduce exposure to lead
Administrative control information and records will be maintained as an addendum to this written program.
Respirators
When respirators are used to supplement engineering and work practice controls to comply with the PEL and all other requirements have been met, employee exposure, for the purpose of determining compliance with the PEL, may be considered to be at the level provided by the protection factor of the respirator for those periods the respirator is worn. Those periods may be averaged with exposure levels during periods when respirators are not worn to determine the employee's daily TWA exposure. The respiratory protection program will be conducted in accordance with 29 CFR 1910.134 (b) through (d) (except (d)(1)(iii)), and (f) through (m). The company will provide a powered air-purifying respirator when an employee chooses to use this type of respirator and such a respirator provides adequate protection to the employee.
Respirators must be used during:
• Periods necessary to install or implement engineering or work-practice controls.
• Work operations for which engineering and work-practice controls are not sufficient to reduce employee exposures to or below the permissible exposure limit.
• Periods when an employee requests a respirator
Protective Clothing & Equipment
If an employee is exposed to lead above the PEL, without regard to the use of respirators or where the possibility of skin or eye irritation exists, the company will provide at no cost to the employee appropriate protective work clothing and equipment such as, but not limited to:
• Coveralls or similar full-body work clothing;
• Gloves, hats, and shoes or disposable shoe coverlets; and
• Face shields, vented goggles, or other appropriate protective equipment
Cleaning and replacement - the company will:
• provide the protective clothing in a clean and dry condition at least weekly, and daily to employees whose exposure levels without regard to a respirator are over 200 ug/m(3) of lead as an 8-hour TWA.
• provide for the cleaning, laundering, or disposal of protective clothing and equipment
• repair or replace required protective clothing and equipment as needed to maintain their effectiveness.
• assure that all protective clothing is removed at the completion of a work shift only in change rooms provided for that purpose
• assure that contaminated protective clothing which is to be cleaned, laundered, or disposed of, is placed in a closed container in the change-room which prevents dispersion of lead outside the container.
• inform in writing any person who cleans or launders protective clothing or equipment of the potentially harmful effects of exposure to lead.
• assure that the containers of contaminated protective clothing and equipment required by paragraph (g)(2)(v) are labeled as follows: CAUTION: CLOTHING CONTAMINATED WITH LEAD. DO NOT REMOVE DUST BY BLOWING OR SHAKING. DISPOSE OF LEAD CONTAMINATED WASH WATER IN ACCORDANCE WITH APPLICABLE LOCAL, STATE, OR FEDERAL REGULATIONS.
• prohibit the removal of lead from protective clothing or equipment by blowing, shaking, or any other means which disperses lead into the air.
Housekeeping
• All surfaces shall be maintained as free as practicable of accumulations of lead.
• Floors and other surfaces where lead accumulates may not be cleaned by the use of compressed air.
• Shoveling, dry or wet sweeping, and brushing may be used only where vacuuming or other equally effective methods have been tried and found not to be effective.
• Where vacuuming methods are used, the vacuums shall be used and emptied in a manner which minimizes the reentry of lead into the workplace.
Hygiene Facilities & Practices
The following is requirements pertain to all areas where employees are exposed to lead above the PEL, without regard to the use of respirators:
• No storage or consumption of food or beverages
• No tobacco product storage or use
• No cosmetics stored or used
• No personal clothing or articles, except in authorized change areas
Change rooms
Clean change rooms are provided for employees who work in areas where their airborne exposure to lead is above the PEL. Change rooms are equipped with separate storage facilities for protective work clothing and equipment and for street clothes which prevent cross-contamination. Employees who are required to shower after work shifts are not allowed to leave the workplace wearing any clothing or equipment worn during the work shift.
Showers
Employees who work in areas where their airborne exposure to lead is above the PEL must shower at the end of the each work shift.
Lunchrooms
Separate lunchroom facilities are provided for employees who work in areas where their airborne exposure to lead is above the PEL. These facilities are temperature controlled, have positive pressure and filtered air supply, and are readily accessible to employees. All affected employees must wash their hands and face prior to eating, drinking, smoking or applying cosmetics in the lunchroom area. Employees may not enter lunchroom facilities with protective work clothing or equipment unless surface lead dust has been removed by vacuuming, down draft booth, or other cleaning method.
Lavatories
An adequate number of separate lavatory facilities are maintained for employees who work in lead controlled process areas.
Signs
Proper signs will be posted at the entrance and exits to all lead hazard areas, No other signs or statements may appear on or near any lead hazard sign which contradicts or detracts from the meaning of the required sign. All lead hazard signs will be kept illuminated and cleaned as necessary so that the legend is readily visible. The signs will contain the following or other appropriate wording/warning:
WARNING
LEAD WORK AREA
POISON
NO SMOKING OR EATING
Employee Training
All affected employees will participate in the company Lead Safety Training program. All affected employees will be trained prior to the time of initial job assignment and at least annually.
Employee training will consist of:
• specific OSHA requirements contained in
◦ 1910.1025 - OSHA Lead Standard
◦ 1910.1025 App A - Substance data sheet for occupational exposure to lead
◦ 1910.1025 App B - Employee standard summary
• specific nature of the operations which could result in exposure to lead above the action level
• purpose, proper selection, fitting, use, and limitations of respirators;
• purpose and a description of the medical surveillance program, and the medical removal protection program including information concerning the adverse health effects associated with excessive exposure to lead (with particular attention to the adverse reproductive effects on both males and females);
• engineering controls and work practices associated with the employee's job assignment;
• contents of the company compliance plan
• instructions that chelating agents should not routinely be used to remove lead from their bodies and should not be used at all except under the direction of a licensed physician
• materials pertaining to the Occupational Safety and Health Act
A copy of the OSHA standard 1910.1025 and its appendices will be readily available to all affected employees.
Medical Surveillance
The company has instituted a medical surveillance program for all employees who are or may be exposed above the

GET INSTANT ACCESS
to THE MEMBERS LIBRARY
Safety materials created by safety professionals.
Access to the Safety Manager software.
Wide variety of safety videos and courses.
**Brand New** Safety Training Management System
Pre-Made Safety Materials Ready For Use
Created by experienced safety professionals & risk consultants. Saving you time, money, and risk of injuries.
95% of the work already done.
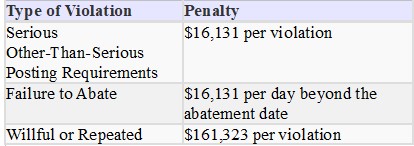
Below are the maximum penalty amounts, with the annual adjustment for inflation, that may be assessed after Jan. 15, 2024. (See OSHA Memo, Jan. 8, 2024).
**New OSHA HEAT 90 DAY**
>>Download Free HERE<<
**New 2024 OSHA 300 Form**
>>Download Free HERE<<
**Brand New**
Free with full membership subscription
Training LMS System
Ask The Safety Consultant
Safety Equipment Deal Finder

“SafetyInfo.com is the first go-to website for safety professionals and companies to use in establishing a solid safety program"
-Mike McKenzie, Certified Safety & Health Manager (CSHM), McSafety Solutions™
Note: You must have a full subscription to the Safety Library in order to use this material. Any use outside of your organization, for resell, or without an active membership is strictly prohibited and may result in prosecution under copyright infringement laws. Please contact us first, if you would be interested in reselling or using our materials for reproduction.
Inside the Members Library
Topic Index
Accident Prevention
Air Quality
Asbestos
Bloodborne Pathogens
Boilers
Chemical Safety
Compressed Gas
Confined Space
Construction
Construction Worksite
Cranes & Slings
Driver / Fleet Safety
Drug Free Workplace
Electrical
Emergency Management
Engineering Safety
Environmental
Equipment
Ergonomics
Fall Protection
Fire Safety & Prevention
First Aid
Flammable Materials
Forklifts
Hazard Communication
Hazardous Materials
Hearing Protection
Heat Stress
Hot Work
Housekeeping
Job Safety Analysis
Laboratory
Ladders
Lead
Lockout-Tagout
Machinery & Equipment
Material Handling
MSDS (SDS)
Medical & First Aid
Occupational Health
Office Safety
Off the Job Safety
Personal Protection
Process Safety
Record Keeping
Respiratory Protection
Silica Safety
Rules & Policies
Signs & Labels
Slips, Trips & Fall
Training
Terrorism Programs
Tool Safety
Vehicle & Driver
Violence Programs
Welding & Hot Work
Training Videos
Library Index
Training Materials
Videos/Courses
Talks
Articles
PowerPoint
Handouts
Training Overheads
Quizzes
Supervisor Briefs
Management Briefs
Safety Sessions
2 Minute OSHA Safety Talks
Pamphlets
First Aid Training
Supervisor Training
Hazardous Materials
Bomb Threat
Crossword Puzzles
Biological Agents
Forms & Documents
Forms
Checklists
Audit Guides
Inspections Guides
Signs & Labels
Environmental Audit Guides
Recordkeeping - OSHA 300
Sign & Label Maker
Safety Management Resources
Safety Manuals/Written Programs
Ergonomic Programs
Emergency Plans
Process Safety Management
Construction Safety
Occupational Health
Environmental
Topic Sheets
DOT Fleet-Driver
Hazardous Materials
Chemical Safety
Drug Free Workplace
Terrorism Programs
Development Guides
Safety Manager Software
Safety References & Graphics
Technical Safety Information
Posters
Topic & Fact Sheets
Development Information
Job Specific Safety Rules
Terrorism
Calculators
Safety Comic Strips
New Safety Training System
Schedule and train your employees with our materials. Add unlimited amount of employees. Record all progress and issue certificates. For group and individual training sessions.

